The process of classical conditioning can explain how we acquire phobias. A natural response to something unfamiliar new and unexpected falls under the first stage of the classical conditioning theory.

Classical Conditioning How It Works And How It Can Be Applied
Classical conditioning is a process that entails having a neutral pointer before a reflex.

. In this process the person with the phobia is. What Are The Principles Of Classical Theory In Criminology. This type of theory was first developed around John Watson and his outlook on behaviorism where he argued that a persons behavior can be studied without any reference to the mind.
When a neutral stimulus something that does not cause fear is associated with an unconditioned stimulus something that causes fear. One of the first studies to test the possibility of applying classical conditioning to the. Furthermore operant conditioning as a concept deals with the strengths and weaknesses that surround voluntary behaviors.
According to classical-conditioning theory phobias develop as the result of. On the other hand operant conditioning involves the use of reinforcement after a stated behavior. Classical conditioning is used both in understanding and treating phobias.
While initially the neutral stimulus of water had no connection to fear the event changed the way they viewed water. After an association has formed the dog now a conditioned stimulus causes a response. The process then leads to the response of fear towards the previously neutral stimulus.
Many phobias develop as a result of having a negative experience or panic attack related to a specific object or situation. There may be a link between your own specific phobia and the phobia or anxiety of your parents this could be due to genetics or learned behavior. Vicarious and informational transmission of fears can take place in the absence of direct contact with the fear stimuli.
Soon the dog associated the sound with the presence of food. Fear of heights dogs snakes dark. Therefore the sound of a metronome was enough for the dog to produce salivation because it had associated the sound with the presence of food and this response is called a.
How Classical Conditioning Works. Conditioning is the process of pairing two stimuli together so that if one stimulus can trigger a reaction the other can do the same too simply by association. Watson Rayner 1920 were the first psychologists to apply the principles of classical conditioning to human behavior by looking at how this learning process may explain the development of phobias.
Fear is a behavior that can be learned via classical conditioning. In order to understand more about how classical conditioning works it is important to become familiar with the basic principles of the process. According to classical-conditioning theory phobias develop as the result of by systematically desensitizing the threat through the introduction of new conditioned responses How might behavioral techniques help treat phobias.
The neutral stimulus that doesnt. This is the first response produced by an unconditioned stimulus. The classical conditioning theory states that through a process of learned association the conditioned stimulus will be paired with the unconditioned stimulus and a conditioned behavioural response will then occur when the paired unconditioned stimuli is presented alone.
Criminals make rational choices and choose to commit crimes for maximum pleasure and minimum pain according to classical thinking. Classical conditioning is a theory of pairing one stimulus with another neutral stimulus that causes changes in the response to the neutral stimulus Goldstein. Fear conditioning is a type of classical conditioning that involves pairing an aversive stimulus such as an electric shock with either a neutral context such as a location or stimulus such as a tone.
Criminals are rational they weigh up the costs and therefore we should create deterrents that are slightly more effective than what would be gained by the. Classical conditioning can also be used to treat phobias in a process known as desensitization. This is the process of how classical conditioning and phobias are formed.
According to classical-conditioning theory phobias develop through the generalization of the a fear experience as when a person stung y. Here are a few examples of classical conditioning in the classroom. How phobias are formed.
Before conditioning refers to an unlearned response to an unconditioned stimulus. They did this in what is now considered to be one of the most ethically dubious experiments ever conducted the case of Little Albert. Bur if the teacher claps 3 times the children.
Classical conditioning involves forming an association between two stimuli resulting in a learned response. This results in the expression of a fear response in the. It is suggested that fears can be acquired by three pathways.
For example we learn to associate something we do not fear such as a dog neutral stimulus with something that triggers a fear response such as being bitten unconditioned stimulus. The conditioning could be evoked by the sound of a metronome and whenever the dog was fed the sound was played. A phobia is an excessive irrational fear to something specific like an object or situation.
Water is now connected to fearand the traumatic situation experienced years ago eternally linked this negative response with this particular stimulus. Albert Bs mother was a wet. Specification of a fear experience.
How Phobia can be learned through Classical Conditioning. Conditioning vicarious exposures and by the transmission of information and instruction. It doesnt mean a new behavior has been adopted.
An acquired fear that is out of proportion to the real threat of an object or situation. If the teacher instructs the children to keep quiet they keep quiet. There are three basic phases of this process.
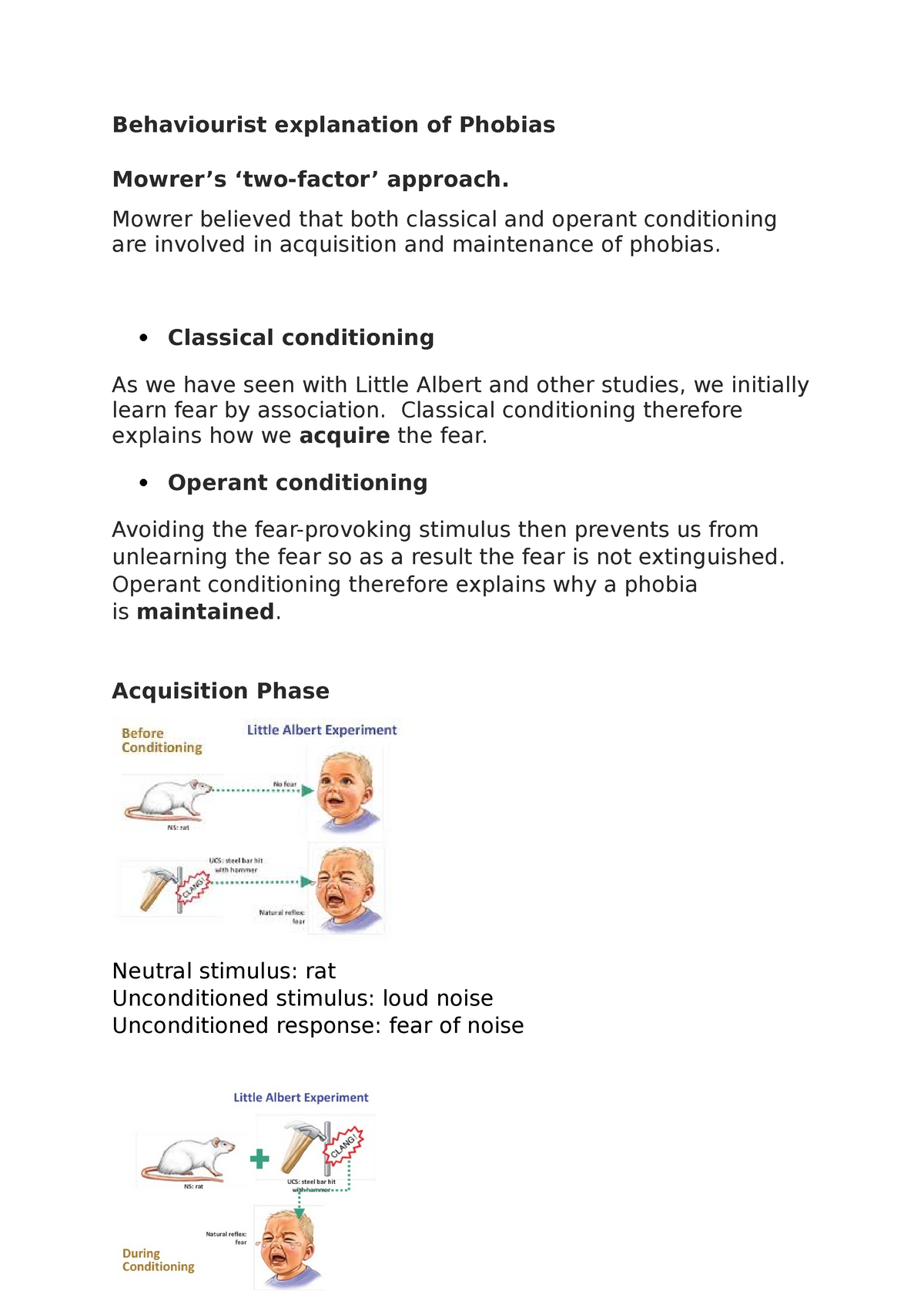
Behaviourist Explanation Of Phobias Lecture Behaviourist Explanation Of Phobias Mowrer S Studocu
Pdf Classical Conditioning And The Acquisition Of Human Fears And Phobias A Review And Synthesis Of The Literature

Psychology One Pager Mind Map Psychology Notes Psychology Terms Study Flashcards
0 Comments